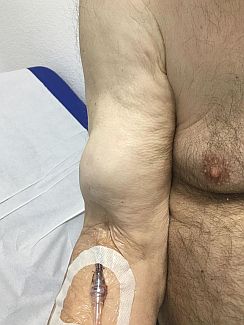
(BMJ)—An 83-yo man w/ DM, hypertension, chronic kidney dz, and asthma was admitted for community-acquired pneumonia. Home meds: candesartan, gliclazide, metformin, simvastatin, inhaled fluticasone/salmeterol. He improved on IV levofloxacin and ceftriaxone, but he experienced sudden right arm pain and swelling on day 4. What is the dx?
|
Extravasation injury
|
|
Bicipitoradial bursitis
|
|
Proximal biceps avulsion
|
|
Brachial artery aneurysm
|
|
Morel-Lavallee lesion
|
(BMJ)—A 27-yo woman presented w/ a 7-yr hx of a progressively worsening, edematous plaque over her L eyelid that was aggravated by sunlight. Review of sx: no joint pain/muscle weakness/mouth ulcers/hand lesions. Exam: visual acuity and eye movement normal. Labs: raised LDH. What is the dx?

|
Polymorphous light eruption
|
|
Periorbital cellulitis
|
|
Amyopathic dermatomyositis
|
|
Discoid lupus erythematosus
|
|
Cavernous sinus thrombosis
|
(BMJ)—A 49-yo man w/ hypertension under medical control presented to the ED w/ sudden chest pain, dyspnea, and diaphoresis. Exam: low blood pressure. Abdomen: distended w/ mottled skin. ECG: no ST elevation. What is the dx?

|
Pancreatitis
|
|
Perforated viscus
|
|
Pulmonary embolism
|
|
Myocarditis
|
|
Aortic dissection type A
|
(BMJ)—A 62-yo woman presented w/ a right axillary lesion that had grown over 13y from an itchy, coin-sized plaque presumed to be eczema. The lesion was occasionally painful and would bleed. Exam: red-brown plaque w/ erosion; nontender axillary and supraclavicular nodes. Bx confirmed the dx. What is it?

|
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
Erythrasma
|
|
Extramammary Paget dz
|
|
Erythema intertrigo
|
|
Parapsoriasis
|
