(BMJ)—A 7-yo boy presented w/ a large painless blister on his tongue, which was bifid. He had hx of recurrent traumatic mouth ulcers and tongue trauma, self-extraction of secondary teeth, self-avulsion of finger nails, multiple painless fractures resulting in Charcot joints of the left knee and ankle, mild learning difficulties, and impulsive behavior. Parents are 1st cousins. What is the dx?

|
Nonaccidental trauma
|
|
Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome
|
|
Neurofibromatosis type 1
|
|
Behcet syndrome
|
|
Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 4 (HSAN IV)
|
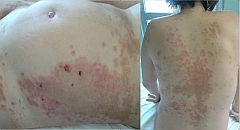
(BMJ)—A 32-yo nulliparous woman presented at 33wk gestation w/ intense pruritus of 1mo duration. There had been no improvement after tx for scabies. Exam: extensive erythematous plaques w/ targetoid lesions, vesicles, and bullae on abdomen, trunk, and all extremities. Labs: mild anemia, LFTs WNL. What is the dx?
|
Polymorphic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy
|
|
Dermatitis herpetiformis
|
|
Impetigo herpetiformis
|
|
Erythema multiforme
|
|
Pemphigoid gestationis
|
(BMJ)—A 26-yo man presented w/ a 7-wk hx of an ulcer on his L elbow that was increasing in size. It had not improved after a course of oral floxacillin. He did not recall any trauma and did not have fever, wt loss, or other lesions. He had been to the Peruvian Amazon 3mo prior. Exam: 2x3-cm ulcer w/ lymphangitis ascending to axilla. What is the dx?

|
Cutaneous leishmaniasis
|
|
Orf
|
|
Tropical pyoderma
|
|
Pyogenic granuloma
|
|
Mycobacterium marinum
|
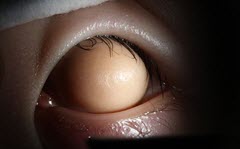
(BMJ)—A 17-mo boy had a soft, painless mass in the L eye since birth that gradually increased in size. Exam: mass w/ skin-like surface; the mass covered the cornea and protruded beyond the palpebral fissure. What is the dx?
|
Corneal dermoid
|
|
Staphyloma
|
|
Juvenile xanthogranuloma
|
|
Foreign body granuloma
|
|
Osseocartilaginous choristoma
|
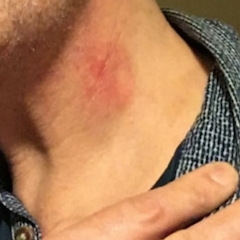
(BMJ)—A 55-year-old man presented with sudden-onset R-sided weakness and aphasia. A squash ball had hit him in the neck 2 weeks prior. Exam: contusion, L anterior neck; expressive dysphasia; R arm and leg weakness. What’s the dx?
|
Carotid artery dissection
|
|
Vertebral artery dissection
|
|
Venous sinus thrombosis
|
|
Complicated migraine
|
|
Anterior cord syndrome
|
