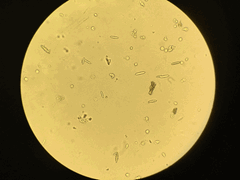
(BMJ)—A 52-yo man was brought to the ED w/ confusion & SOB. Exam: agitated; RR, 28/min. Labs: VBG: pH 7.02, pCO2 26, pO2 31; lactate, 59 mg/dL; glucose, 128 mg/dL; anion gap, 19 mEq/L; creatinine, 1.6 mg/dL; osmolality, 318 mOsm/kg; osmolal gap, 20 mOsm/kg; EtOH neg; UTox neg; UA: (+)blood, (-)ketones; urine micro: (+)crystals. What is the dx?
|
Methanol poisoning
|
|
Isopropyl alcohol poisoning
|
|
Propylene glycol poisoning
|
|
Ethylene glycol poisoning
|
|
Diethylene glycol poisoning
|
