(BMJ)—An otherwise healthy 3-mo boy born full-term by normal vaginal delivery had progressive hair loss in a band across his occiput x1mo. Exam: positive hair pull test. Trichoscopy: reduced hair density, preserved follicular ostia, and telogen hairs. What is the dx?

|
Halo scalp ring
|
|
Cephalohematoma
|
|
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn
|
|
Neonatal occipital alopecia
|
|
Pressure alopecia
|
(BMJ)—A 51-yo woman w/ prior L eye trauma and fungal infection presented w/ L eye pain, light sensitivity, and inability to close the eyelid. In the L eye, her best corrected visual acuity was reduced to hand motion; in the R eye, visual acuity was 20/40. Intraocular pressure: WNL. L eye: severe conjunctival injection, protruding blue lesion w/ iridocorneal adhesions. What is the dx?

|
Uveal melanoma
|
|
Acquired anterior staphyloma
|
|
Scleromalacia
|
|
Buphthalmos
|
|
Coloboma
|
(BMJ)—A 12-yo boy presented w/ progressive darkening of fingernails and toenails x3mo. There was no hx of exposure to dyes and no trauma. Exam: blue-black nails w/ hyperpigmented nail beds and distal phalanges. Labs: Hgb, 10.9 g/dL. Adrenocorticotropic hormone level WNL. What is the dx?

|
HIV infection
|
|
Iron deficiency
|
|
Wilson dz
|
|
Onychomycosis
|
|
Vitamin B12 deficiency
|
(Epocrates)—A 35-yo female w/ no significant PMHx reported constant numbness and tingling in the 1st and 2nd digits of her R foot after spending 3 days at a rodeo. She experienced no pain or radiation, and her ROM was normal. She admitted to having “a few drinks” of alcohol but had no hx of illicit drug use. Her physical exam was unremarkable, and routine lab tests were all negative. What is the dx?
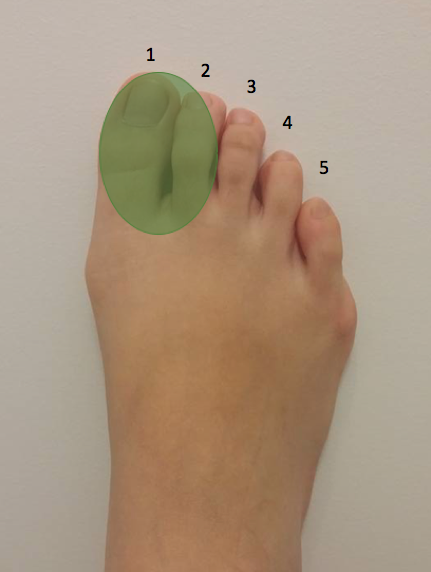
|
Herniated disc
|
|
Diabetic neuropathy
|
|
Compression neuropathy
|
|
Alcohol-induced palsy
|
|
Fibromyalgia
|
(BMJ)—A 41-yo man presented w/ a 6-day hx of unilateral L eye pain after a caterpillar fell into his eye while he was on an adventure vacation. He had initially sought medical attention in the U.S., where multiple foreign bodies were seen on exam, and he was treated w/ chloramphenicol eye ointment. On re-presentation in the U.K.: visual acuity, 20/20. Eye exam: Optic disc and macula normal. Multiple setae (fibers from caterpillar) noted in conjunctiva and eyelids. Multiple corneal abrasions. What is the dx?

|
Phlyctenular keratoconjunctivitis
|
|
Chloramphenicol-related allergic keratoconjunctivitis
|
|
Pinguecula
|
|
Ophthalmia nodosa
|
|
Ocular leishmaniasis
|
