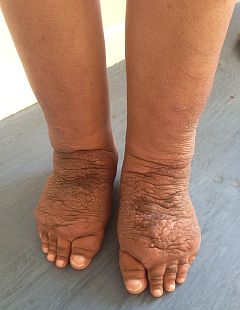
(BMJ)—A 26-year-old woman with Graves' disease and ophthalmopathy presented with progressive bilateral leg swelling for 3 months. Exam: gross thickening and folding of skin on feet, and edema of shins. What’s the dx?
|
Lymphatic filariasis
|
|
Milroy syndrome
|
|
Lichen amyloidosis
|
|
Pretibial myxedema
|
|
Lichen myxedematosus
|
(BMJ)—An otherwise healthy 29-year-old parachutist presented with sudden-onset facial flushing, dizziness, and a diffuse rash that began on a hot day, 1 hour after eating tinned tuna. The symptoms appeared while she was ascending in an aircraft, before a parachute jump from 10,000 feet. She completed the jump uneventfully. What's the dx?

|
Heat-related eruption
|
|
Decompression sickness
|
|
Fish allergy
|
|
Stress-induced urticaria
|
|
Scombrotoxin poisoning
|
